Consolidating Evaluation Tooling
| Status | Authors | Coach | DRIs | Owning Stage | Created |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ongoing |
tle_gitlab
achueshev
|
eduardobonet
|
oregand
|
devops ai-powered | 2024-07-22 |
Summary
This blueprint proposes consolidating our evaluation tooling ELI5 and Prompt Library to create a unified evaluation solution and an accessible way for teams to efficiently evaluate their AI-powered features. As the main outcome, the blueprint presents the idea of merging ELI5 and Prompt Library into the Prompt Library repository and ultimately transforming Prompt Library into an engine, retaining the best features of both products.
Motivation
Over time, GitLab developed two evaluation tools that address the same problem of evaluating AI features but solve this problem differently: Prompt Library, focused on dealing with large scale evaluation, and ELI5, focused on allowing developers to run quick evaluations.
Overview of Prompt Library
Prompt Library is a feature-rich evaluation tool primarily designed for large-scale evaluations and managing large datasets. It was built based on Apache Beam and can be run both locally or in a GCP project using the Dataflow executor. The diagram below demonstrates the internal design of Prompt Library:
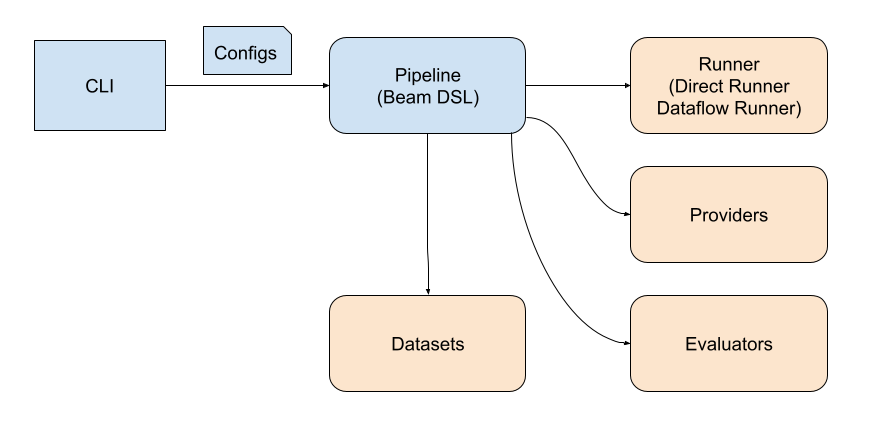
Prompt Library provides a CLI interface to run Apache Beam evaluation pipelines that read datasets from BigQuery tables and output results back to BigQuery. Prompt Library supports a rich configuration system through JSON configuration files that allow engineers to tune various parameters related to LLM judges and other heuristics.
Limitations: Prompt Library components are tightly coupled to the Apache Beam API. Any evaluator requires a deep understanding of the Apache Beam API and BigQuery. Please note that Apache Beam is initially designed for scaled processing, and its programming logic may differ from pure Python development. For example, Apache Beam doesn’t support sorting in the classical sense. This complexity in extending and updating Prompt Library components is currently causing confusion among teams and creating a barrier to adoption for simpler evaluation tasks.
Overview of ELI5
ELI5 is an evaluation tool built on top of LangSmith, primarily designed for fast prototyping and building
evaluation pipelines with less complex component interaction. ELI5 runs locally and requires developers to
clone the repository and install dependencies using poetry. If developers need to run ELI5 remotely, they
need to perform additional manual steps. The diagram below demonstrates the internal design of ELI5:
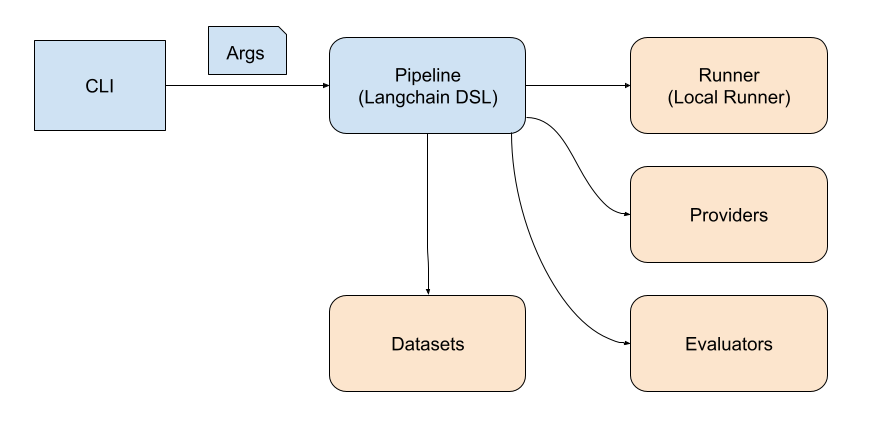
Similar to Prompt Library, ELI5 provides a CLI interface to run evaluations, reading data from LangSmith and outputting results back to LangSmith. LangSmith provides a rich UI that allows developers to effectively analyze results and compare experiments to identify metric drift. The ELI5 CLI supports passing arguments to configure evaluation pipelines. Most of the arguments have default values to reduce the burden on developers and provide earlier results. To further help developers with prototyping evaluation pipelines, ELI5 provides basic building blocks to build evaluators with a unified signature, that is, compare actual output with expected. Depending on the developer’s use case, these evaluators can be a pure Python function, LLM judge, or another LangChain runnable.
Limitations: ELI5 solely relies on LangSmith and is limited by its capabilities. ELI5 helps developers efficiently implement evaluators; however, the execution is out of our control, which may be required for advanced use cases.
Conclusion: Moving Towards a Unified Evaluation Approach
Developing both projects simultaneously is inefficient. It increases the need for maintainers, which is already a bottleneck, and creates barriers for contributions. Additionally, it fosters unnecessary competition and repetition between the tools.
Both projects have their own pros and cons. Prompt Library is a powerful tool for custom evaluation at scale but is not flexible for company-wide contributions and adding new changes. On the other side, ELI5 is a user-friendly solution focused on building the evaluation logic with LangSmith UI support to investigate results. At the same time, ELI5 is limited to the LangSmith platform in terms of using it as an engine. Therefore, consolidating our evaluation tooling is important to keep delivering high-quality results.
Goal
Consolidate evaluation tooling to provide a user-friendly and transparent way for teams to evaluate their AI-powered features.
Objectives
Based on the goal and motivation, we define the following objectives:
-
Integrate ELI5 into Prompt Library by converting Prompt Library into an engine: This integration is crucial for creating a unified, powerful, and user-friendly Centralized Evaluation Framework (CEF). The goal is to create a flexible foundation that allows developers to focus on building pure Python function evaluators and running them on the Prompt Library engine, similar to LangSmith.
-
Enhance flexibility, extensibility, and user-friendliness: This objective ensures that the consolidated tool is adaptable to diverse needs and accessible to developers with different skill sets. The result is reducing barriers to entry but offering the power and flexibility to meet the diverse needs of different teams, from quick prototyping to extensive evaluations.
-
Improve documentation and user guidance: Clear documentation and user guidance are essential for successful adoption and effective use of the consolidated tool. This reduces the learning curve, minimizes user errors, and enables teams to leverage the full potential of the evaluation capabilities.
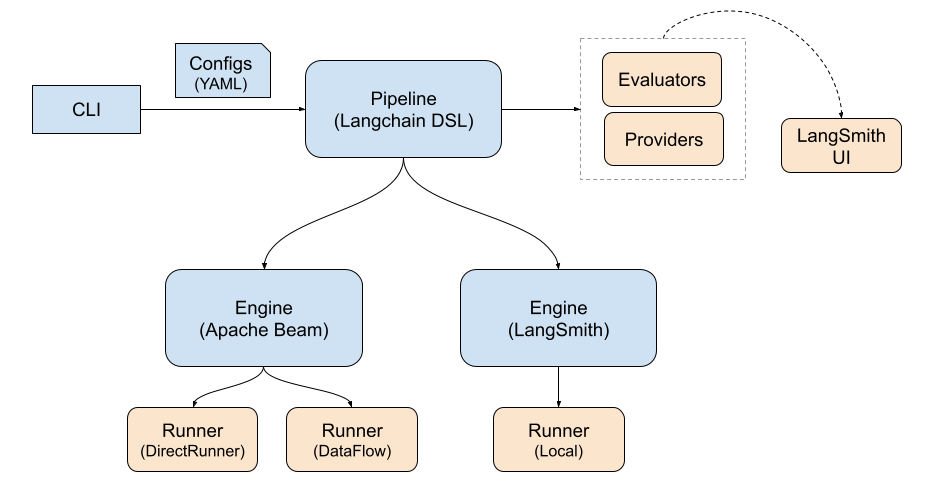
As an outcome, the consolidated tool after completing the defined objectives can be represented as follows:
Non-goals
Dataset management
Dataset management and creation are not considered primary objectives within the scope of this proposal. These aspects are addressed in a separate issue: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/modelops/ai-model-validation-and-research/ai-evaluation/prompt-library/-/issues/349. In this proposal, we assume that the necessary data for running evaluations is already available in the dataset Single Source of Truth (SSOT), which is accessible to the consolidated solution.
AI Gateway integration
Centralizing model access through AI Gateway enhances consistency, reduces maintenance overhead, and minimizes the risk of errors associated with managing multiple model access points. Connecting AI Gateway may improve overall system reliability and efficiency. However, integrating AI Gateway into the consolidated tool doesn’t appear to be a strict requirement to achieve the main goal. We plan to explore this task further once ELI5 and Prompt Library are successfully integrated.
Apache Beam as Prompt Library executor
Prompt Library relies on Apache Beam to run the evaluation pipelines. Apache Beam was originally designed for other tasks such as processing at scale and therefore is sometimes a bottleneck when implementing evaluation logic. The Model Validation group has already been looking into replacing Apache Beam with another solution to run the evaluation pipelines. However, to better manage technical debt at this stage and consolidate tooling with fewer code base changes, we have decided to continue using Apache Beam. We are designing the consolidated tool in a way that keeps evaluators simple and decoupled from the Prompt Library’s internal logic. This approach will allow us to revisit the rationale behind using Apache Beam once we complete the consolidation work.
Implementation steps
This section describes the implementation steps we need to perform to achieve the objectives defined in the previous section. Please note that we define the implementation steps following GitLab Values - Collaboration, Efficiency, Iteration, and Transparency. Every step can be later converted into an epic or an individual issue depending on complexity.
1. Move ELI5 as a folder into the Prompt Library repository
This step consolidates code without immediate alterations, facilitating the identification of duplicate code and reducing the number of required maintainers. It also increases the visibility of Prompt Library while maintaining existing functionality for current users of both tools.
The process involves relocating the ELI5 folder structure into the Prompt Library repository and updating documentation to reflect the new repository location.
User Impact:
- Existing functionality remains unchanged for both ELI5 and Prompt Library users.
- ELI5 users clone the Prompt Library repository instead of the separate ELI5 repository.
- The ELI5 repository is archived and no longer receives new updates.
Estimated time: < 1 milestone.
2. Convert Prompt Library into an engine
This step focuses on preparing the Prompt Library code base for integration with the existing ELI5 logic. The goal is to convert Prompt Library into a basic engine that accepts ELI5-compatible evaluators.
The process involves updating the Prompt Library code base, providing a Python API similar to LangSmith used by ELI5. This conversion allows developers to focus on pure evaluation logic without needing to interact directly with Apache Beam. We aim to keep Prompt Library’s key strength, that is, customization and running at scale.
User Impact:
- Existing functionality remains unchanged for both ELI5 and Prompt Library users.
- Prompt Library maintainers need to support the previous old highly-coupled evaluation pipelines, fixing bugs only.
- If new evaluation logic needs to be implemented, developers implement ELI5-compatible evaluators and use them with the new Prompt Library engine.
Estimated time: 1-1.5 milestone.
3. Power existing ELI5 evaluators with the Prompt Library engine
This step adds an additional option for ELI5 developers to run their existing evaluators with the Prompt Library engine. By completing this step, we connect the ELI5 codebase to Prompt Library, allowing developers to prototype their evaluation pipelines quickly and also implement advanced custom logic if required.
This process involves updating the ELI5 codebase to include an option of triggering the Prompt Library engine.
User Impact:
- Existing functionality remains unchanged for both ELI5 and Prompt Library users.
- ELI5 users receive an additional option to run evaluators on the custom Prompt Library engine if they require.
- ELI5 users interact with Prompt Library as an engine using the Python API similar to LangSmith.
Estimated time: 1 milestone.
Note: This step can be implemented in parallel with converting Prompt Library evaluators to be ELI5 compatible.
4. Convert Prompt Library evaluators to be ELI5 compatible
This step converts the existing Prompt Library evaluators to be ELI5 compatible. The goal is to streamline existing old logic, further merging code bases and mitigating any differences between the two approaches.
This process involves updating the Prompt Library code base. ELI5 already provides basic building blocks to implement various evaluators, including pairwise evaluators or LLM judges. These building blocks can be reused to make corresponding changes to the existing Prompt Library evaluators.
User Impact:
- Existing functionality remains unchanged for both ELI5 and Prompt Library users.
- Prompt Library maintainers support the previous old highly-coupled evaluation pipelines, fixing bugs only.
- If new evaluation logic needs to be implemented, developers implement ELI5-compatible evaluators and use them with the new Prompt Library engine.
Estimated time: 1-1.5 milestone.
Note: This step can be implemented in parallel with powering existing ELI5 evaluators with the Prompt Library engine.
5. Merging CLI interface
Both ELI5 and Prompt Library provide CLI interfaces but with different configuration systems created for different purposes. This step ensures that developers run a single CLI interface with a configuration system that provides default values to run evaluations and is also flexible enough for advanced usage when developers need to update evaluation settings.
This process involves updating the CLI interfaces of both ELI5 and Prompt Library and creating a new configuration system based on YAML files with examples and default configurations to support most of the usual developer needs.
User Impact:
- Existing functionality remains unchanged for both ELI5 and Prompt Library users.
- ELI5 and Prompt Library start providing a single CLI interface to run evaluations.
- ELI5 and Prompt Library maintainers support the old CLI interfaces, freezing any additions.
Estimated time: 1 milestone.
6. Deprecate old ELI5 and Prompt Library logic
This step focuses on deprecating and removing the old evaluation pipelines and related components the maintainers had to support in the previous steps. The goal is to start using the consolidated tool that includes ELI5-compatible evaluators running on the Prompt Library as an engine, the modified CLI, and enhanced configuration system.
User Impact:
- Developers start using ELI5 and Prompt Library as a consolidated tool, that is CEF.
- Developers rely on the new documentation and guidelines for working with the consolidated tool.
- Deprecated dependencies coming from the original ELI5 and Prompt Library projects are successfully cleaned up.
Estimated time: < 1 milestone.
Alternatives
This section presents alternatives that we explored but didn’t pursue due to the reasons specified.
-
Build upon ELI5 and archive Prompt Library ELI5 has attracted more contributors and better supports the current needs of our teams. Instead of merging ELI5 into Prompt Library, we could shelve Prompt Library and expand ELI5 with additional features. However, taking the learnings from ELI5, making Prompt Library more user-friendly is an easier task than applying the scale of Prompt Library to ELI5.
-
Archive ELI5 and Prompt Library and start from scratch. This would allow us to take the learnings from ELI5 and Prompt Library without inheriting their technical debt. However, starting a new solution would take longer to implement and might still lead to unforeseen issues. This approach wouldn’t necessarily save us from technical debt in the long run.
Future evolution
This section presents future ideas we are considering after achieving the main goal of this proposal.
-
Merge Prompt Registry and evaluation repositories. Currently, prompts are being migrated from GitLab-rails into the AI Gateway repo. This is already an improvement over the current setup, but having prompts and evaluations in separate repos is like having GitLab and GitLab unit tests in different repos. Tests (Evaluations) should be run in the same place as the code (prompts). We suggest further moving them together.
-
Evaluation through pipeline CI An alternative user-friendly solution for running evaluations is through GitLab pipelines, as showcased in this prototype: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/ai-powered/custom-models/evaluations/-/jobs/7518078099. Having a consolidated evaluation repository will simplify the implementation of such a feature.
eef3c341)
