Internal releases for GitLab SaaS single tenant instances
Introduction
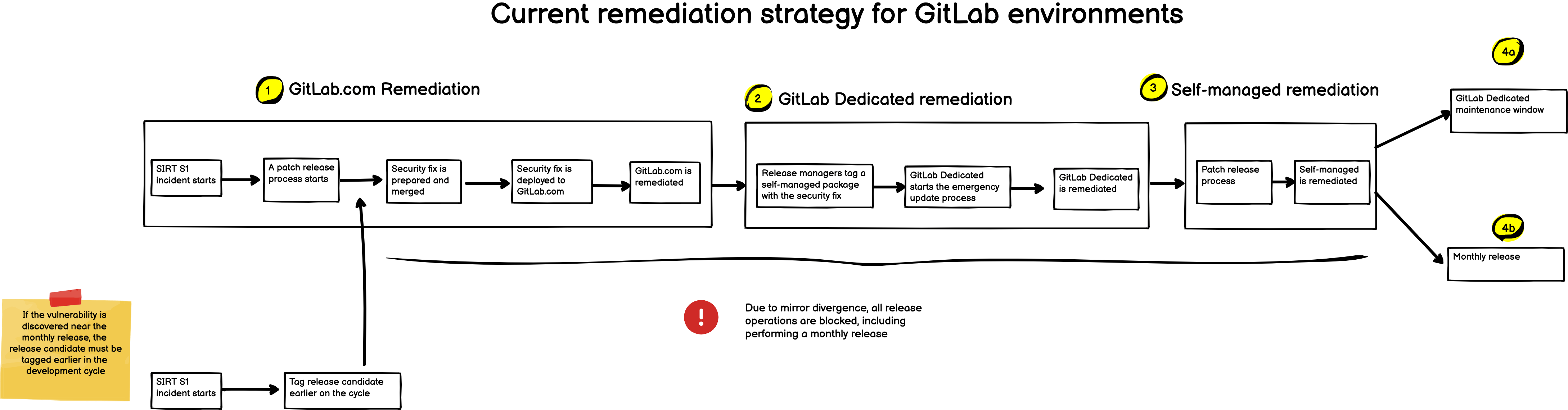
In 2023 GitLab launched a new fully managed private solution, GitLab Dedicated, our single tenant SaaS offering completely managed by GitLab Inc. These internal instances run public GitLab versions limiting the ability to deploy security fixes before a public disclosure. To guarantee the safety and availability on single tenant SaaS instances, Delivery has an increasing need to prepare private packages to remediate high-severity issues within specific SLAs.
There is no official release process available to remediate these private instances. Given the GitLab open core and public by default nature, GitLab releases were designed to be public from the beginning of time. In case of a high-severity issue release managers must manually operate the release tooling available to remediate the single tenant SaaS instances within the remediation SLAs, impacting GitLab customers and the ability to remediate them on time:
- Elevated coordination between release managers and all the stakeholders involved.
- The current release tooling lacks the flexibility to perform simultaneous releases, for example, if a vulnerability is found near the monthly release week preparation, a release candidate must be created earlier on the development cycle, renouncing features and bug fixes for the active monthly release.
- Existing release process are not adept to remediate single tenant Saas instances putting at risk their availability and integrity.
Goal
Introduce an internal release GitLab process focused on releasing private packages targeted to private GitLab SaaS managed instances. Private packages will contain remediations for the high-severity issues before disclosing them to the general audience. Due to the nature of GitLab business model addressing internal releases brings unique long-term challenges that will be driving Delivery-Releases work during the upcoming quarters:
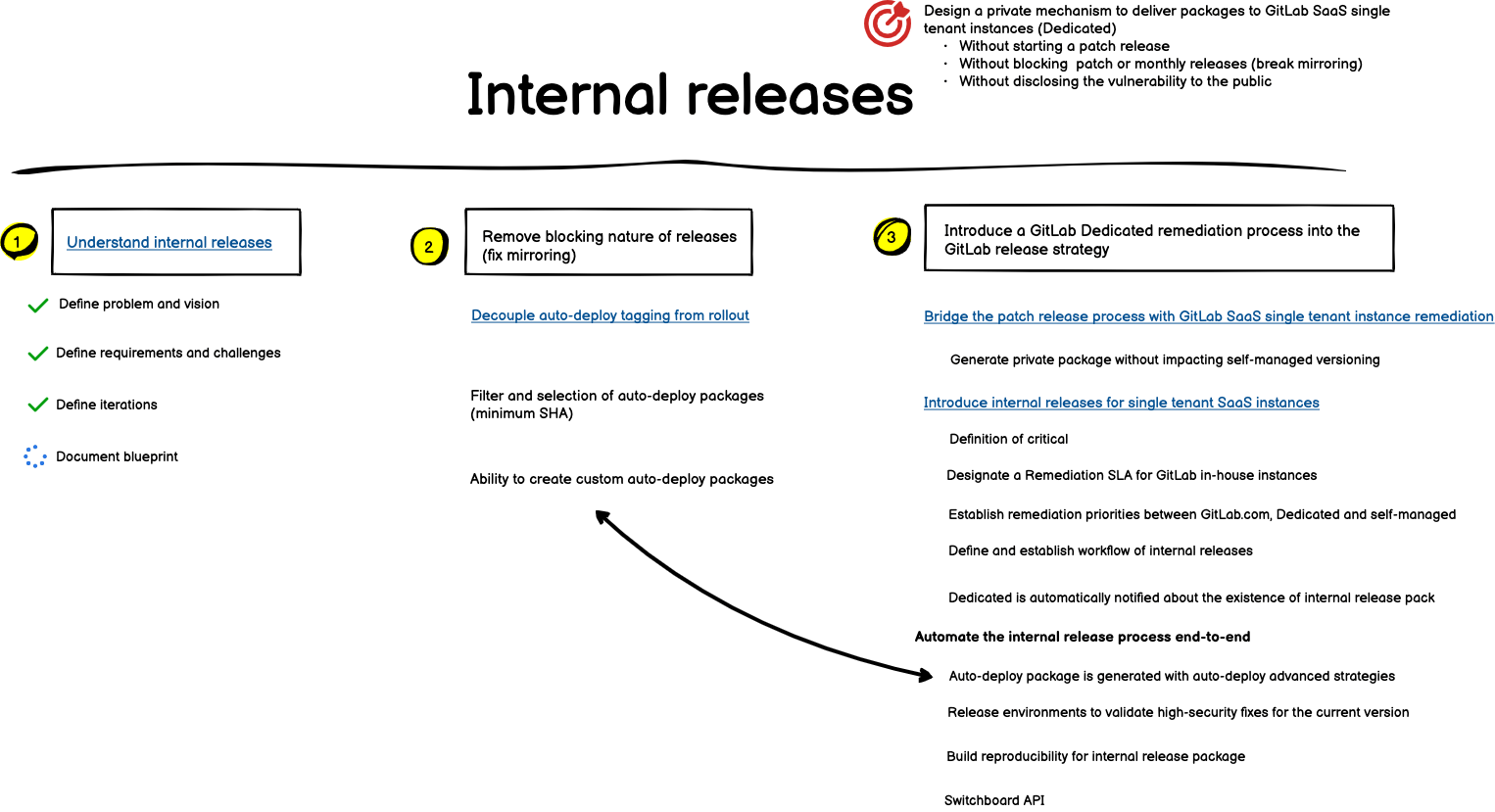
- Understanding the internal release nature. Introducing a private release on top of the GitLab’s open nature by default is a unique challenge that starts by understanding the problem, vision, scope, and challenges. The outcome of this first step is this blueprint that documents the internal release roadmap.
- Remove the blocking nature of releases. Engineering constraints prevent preparing a patch release in the middle of the monthly release week preparation. Establishing a private release process requires removing this constraint with flexible tooling to allow simultaneous releases without leaking vulnerabilities before they’re disclosed.
- Introduce a GitLab Dedicated remediation process into the GitLab release strategy. GitLab SaaS single tenant instances are remediated by manually operating the critical patch release process. This involves considerable toil from release management, security and engineering stakeholders. Internal releases aim to upgrade the GitLab Dedicated remediation process to be at the same level as GitLab.com and self-managed remediation processes.
Key terms
- Internal releases: New private release strategy to remediate GitLab SaaS single tenant instances within specific SLAs.
- GitLab SaaS single tenant instances: SaaS instances managed by GitLab, Inc. At the moment limited to GitLab Dedicated.
- High-severity issues: Bugs or security vulnerabilities defined as ~“severity::1” having an impact on availability, functionality or critical for security on GitLab SaaS single tenant instances.
- See release terminology for additional definitions.
Goals and non-goals
Vision
Short-term
Align the internal releases effort into the GitLab Delivery strategy. Outline a vision, effort, and an understanding of the challenges and requirements to embed an internal release process as part of the GitLab releases. We will deliver this by:
- Documenting a blueprint detailing the roadmap and iterative steps to achieve the internal release vision.
Medium-term
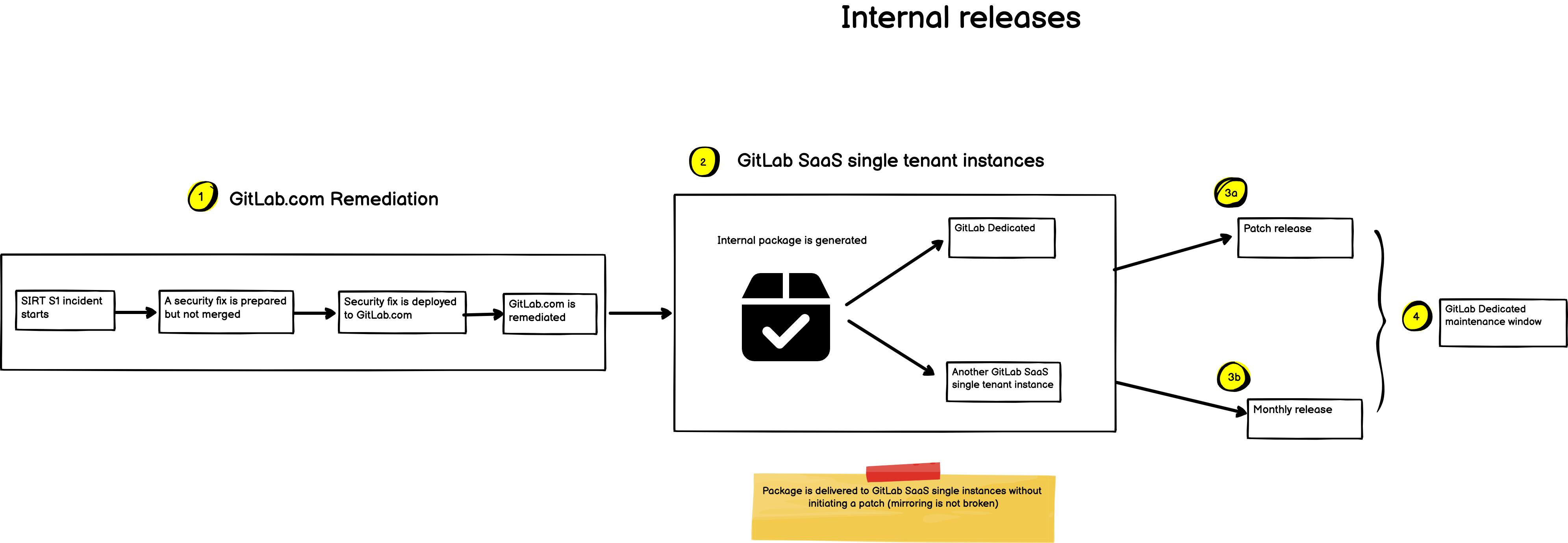
Release Managers will kick off an automated process to create a private release version with the relevant fixes required to remediate GitLab Dedicated without disclosing the vulnerabilities to the public. After the GitLab Dedicated team has sent an acknowledgement that all instances are upgraded, the publish process is then kicked off. We will deliver this by:
- Designing an internal release process to remediate high-severity issues on GitLab SaaS single tenant instances.
- Bridging the patch release process to account for the current GitLab Dedicated remediation strategy. This will permit the generation of a private package with a different tag from the public patch.
- Decouple the current auto-deploy strategy. This will transform release tooling into highly flexible tools and allow to cleanly separate the private and public parts of this process to ensure GitLab Dedicated is running a patched version before any fixes are communicated/released publicly.
Long-term
An internal release process to remediate high-severity issues on GitLab SaaS single tenant instances is part of the GitLab release strategy. Release managers will be able to perform an internal release process to remediate high-severity issues in GitLab SaaS single tenant instances. The outcome of this process will allow GitLab to iteratively deliver fixes to GitLab Dedicated based on the remediation SLAs or when there is a pressing need (short critical remediation targets).
The internal release process should be automated end-to-end, only paging engineers when manual intervention is required, and it should remove the blocking nature of GitLab releases: multiple release types should be performed simultaneously.
- Use advanced package deployment strategies to prepare a private package without blocking an existing release process.
- Emitting private packages without disclosing the vulnerabilities to the general audience.
- Enabling the auto-upgrade of Dedicated tenants via Switchboard API.
Scope
Internal releases are limited to introducing a new release process to SaaS instances managed by GitLab, Inc. At the moment, this is limited to GitLab Dedicated.
Out of scope
- Internal releases are not intended to create releases with custom functionalities that diverge from the standard GitLab product offering.
- Internal releases are limited to mitigate critical vulnerabilities or bug fixes that impact the availability of GitLab SaaS single tenant instances. Issues with lower severity stick to the patch release cadence.
- GitLab.com and GitLab self-managed instances are not considered for internal releases. On these instances, auto-deploy, patch and monthly releases remediate bug and vulnerabilities within the remediation SLAs.
- GitLab Cells is not considered for internal releases, subject to change in the future.
- Internal release channels for self-managed customers are not considered on the initial roadmap. Product analysis and validation will be performed on upcoming stages.
Proposed plan of action
Aside from understanding the internal releases concept and introducing a new internal release strategy, two main requirements must be addressed:
- Remove the blocking nature of GitLab releases.
- Elevate the GitLab Dedicated remediation process to a first-class citizen.
These two requirements can be addressed simultaneously, the work for each will span throughout multiple quarters.
Remove the blocking nature of GitLab releases
The mitigation of a high-severity issue on GitLab.com requires a fix to be merged into the GitLab security repository and deployed to the GitLab production environment. This operation breaks the mirroring between the GitLab canonical and security repositories impeding the monthly release preparation: Performing a monthly release with an undisclosed security vulnerability tampers our ability to remediate GitLab Dedicated and GitLab self-managed instances. Due to this limitation, patch and monthly releases can’t be performed simultaneously without leaking the vulnerability to the public.
The auto-deploy strategy must be adapted to be highly flexible allowing the delivery of packages to all GitLab instances without breaking the mirroring between GitLab repositories and without initiating a patch release. This work will be done in iterations spanning multiple quarters:
- First iteration: Decouple auto-deploy tagging from rollout - Removes the strong coupling between building packages and rolling them out to GitLab.com production environments by establishing two independent processes: one for building packages and another for rolling them out. This iteration paves the way for advanced package selection strategies.
- Second iteration: Filter and selection of auto-deploy packages - With the decoupling of the auto-deploy process, packages can be configured to be built with specific requirements, for example requiring a minimum SHA in all upcoming packages. This ability can be used to guarantee the mitigation of production incidents.
- Third iteration: Ability to create custom auto-deploy packages - The flexibility of auto-deploy should be focused on allowing the creation of packages with experimental features (Ruby/Rails upgrades) or with unmerged changes (security fixes) preventing the mirroring divergence between GitLab repositories.
Introduce a GitLab Dedicated remediation process into the GitLab release strategy
Establish a new private release model for GitLab Dedicated and elevate it to the same standard as GitLab.com and self-managed remediation processes. Considering GitLab open-core nature this is an uncharted territory that will require multiple iterations:
- First iteration: Bridge the patch release process to account for GitLab Dedicated remediation strategy - Adjusts the release tooling to generate self-managed packages without interfering with the patch release process.
- Second iteration: Introduce an internal release process - Design and introduce an internal release process to remediate GitLab Dedicated instances.
- Third iteration: Automate the internal release process end-to-end - With an established internal release process and
with the ability to create custom internal packages:
- The highly flexible auto-deploy process will be used to deploy security fixes without breaking the mirroring between GitLab repositories.
- The internal release process will guarantee predictability and results, and minimize the human factor from the process. The remediation of high severity issues in GitLab Dedicated instances will be automated from start to end by using the Switchboard functionality to perform an auto-upgrade of Dedicated tenants.
c2ee90c8)
